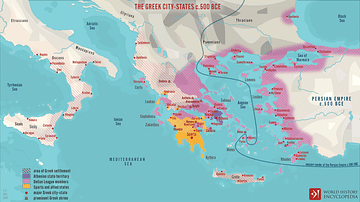
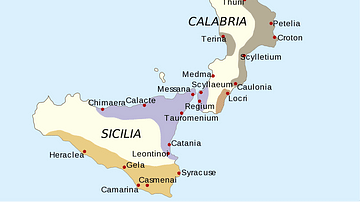
Colonization of the ancient Mediterranean had been taking place since the Bronze Age, especially with Minoan and Mycenaean expansion, but it was the Phoenicians from the 10th century CE that really took the whole idea to a new level. The great Phoenician cities like Tyre established trading posts across the Mediterranean and some of these eventually became such famous places as Carthage and Palermo. From the 8th century BCE, the Greeks started to join the fun and established their colonies in Sicily, southern Italy, and even the Black Sea. Consequently, the food, politics, and cultural practices of the eastern Mediterranean spread further and further west.
The Phoenicians were great traders and great navigators, and this combination of skills almost inevitably resulted in them establishing colonies wherever they went.